Published
•4 min read
Retrieval-Augmented Generation: The Fusion of Retrieval and Generative AI
Explore the world of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), a transformative approach that blends retrieval and generation to create AI systems grounded in real-world knowledge.

Retrieval-Augmented Generation: The Fusion of Retrieval and Generative AI
Imagine an AI system capable of answering complex questions not only with confidence but also with accurate, real-world knowledge. This is the power of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)—a paradigm-shifting approach in artificial intelligence. It combines the knowledge retrieval abilities of search engines with the conversational fluency of generative models to create systems that are both coherent and grounded in truth.
RAG addresses one of the most significant challenges in AI: ensuring that generated outputs are accurate and relevant. From powering advanced chatbots to enhancing decision-making systems, RAG has the potential to redefine how we interact with intelligent systems. Let’s delve into what RAG is, how it works, and why it’s becoming a cornerstone of modern AI.
The Evolution of Retrieval-Augmented Generation
The Birth of RAG
The concept of RAG emerged in response to the shortcomings of traditional AI models:
- Hallucinations: Generative models like GPT could produce plausible but incorrect information.
- Stagnant Knowledge: Generative models trained on static datasets lacked real-time information.
By blending information retrieval (a core capability of search engines) with generative AI, RAG systems offered a solution. Developed and refined by major players like OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft, RAG quickly gained traction for its ability to generate grounded, dynamic responses.
Historical Context
RAG’s emergence built on decades of research in:
- Information Retrieval (IR): Techniques like vector embeddings and similarity search.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): The evolution of encoder-decoder architectures and transformers.
Before RAG, systems either retrieved information (search engines) or generated content (language models). Combining the two bridged the gap, creating AI capable of producing informed and accurate outputs.
The Problem RAG Solves
Grounding Generative AI in Reality
Traditional generative models struggle with hallucinations, creating information that sounds correct but isn’t. Retrieval systems, on the other hand, excel at finding facts but lack conversational depth. RAG unites these strengths:
- Dynamic Knowledge Access: RAG systems retrieve real-time information.
- Contextual Coherence: They generate responses grounded in retrieved data.
Real-World Applications
RAG is transforming industries with its ability to provide accurate, contextually relevant information:
- Healthcare: Assisting doctors with up-to-date medical knowledge.
- Education: Powering personalized learning assistants.
- Legal: Streamlining case research and document analysis.
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation?
RAG is a hybrid AI framework combining two components:
- Retriever: Identifies relevant information from a knowledge base using techniques like vector embeddings and similarity search.
- Generator: Synthesizes the retrieved information into fluent, contextually relevant outputs using advanced NLP models.
Technical Insights
At its core, RAG leverages:
- Vector Search: To match queries with relevant documents.
- Transformer Models: To understand and generate human-like text.
- Encoder-Decoder Architectures: For integrating retrieved data into responses.
How RAG Works
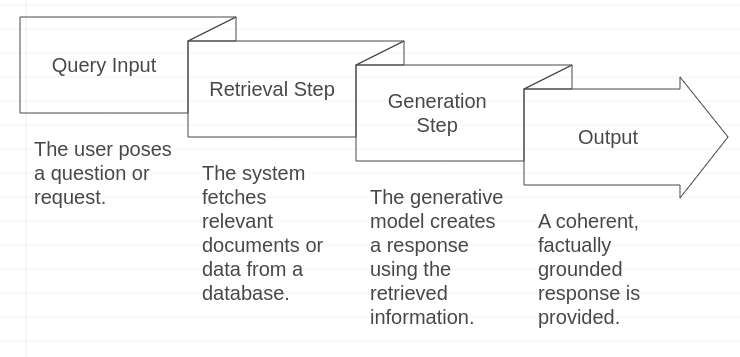
Here’s a simplified view of the RAG workflow:
- Query Input: The user poses a question or request.
- Retrieval Step: The system fetches relevant documents or data from a database.
- Generation Step: The generative model creates a response using the retrieved information.
- Output: A coherent, factually grounded response.
Example: A user asks, “What are the symptoms of Long COVID?”
- The retriever fetches the latest medical articles.
- The generator synthesizes a clear, concise answer using the retrieved data.
Success Stories and Impact
Notable Achievements
- Microsoft Copilot: Enhancing productivity with grounded assistance.
- Google’s Search AI: Revolutionizing search with conversational, accurate responses.
- Legal AI Assistants: Reducing research time for legal professionals.
Comparison to Alternatives
| Feature | RAG | Generative Models Only | Retrieval Systems Only |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High, due to grounding in retrieved data. | Variable, prone to hallucinations. | High, but lacks fluency. |
| Fluency | High, thanks to generative models. | High. | Low, often provides raw data. |
| Real-Time Knowledge | Yes. | No, limited by training data. | Yes. |
The Challenges Ahead
While RAG shows immense promise, challenges remain:
- Scalability: Handling vast, ever-growing knowledge bases.
- Bias Mitigation: Ensuring fairness in retrieved and generated outputs.
- Energy Efficiency: Reducing computational costs.
The Future of RAG
The potential of Retrieval-Augmented Generation is boundless:
- Multimodal Integration: Combining text, images, and video retrieval.
- Real-Time Adaptability: Seamlessly integrating live data streams.
- Ethical AI: Developing systems that prioritize transparency and fairness.
As RAG evolves, it will continue to redefine AI’s role in solving real-world problems, making it a cornerstone of future human-AI collaboration.
Conclusion
Retrieval-Augmented Generation is more than a technical innovation; it’s a leap forward in how AI systems process and present information. By combining the best of retrieval and generative techniques, RAG systems address the limitations of traditional AI, offering accurate, coherent, and grounded responses.
The journey of RAG has only just begun. Whether you’re an AI enthusiast, a researcher, or an industry professional, now is the time to explore this transformative technology and its potential to reshape our world. Ready to dive in? Let’s build the future of intelligent systems together.